【JS】Floyed 求解任意两点之间的最短路径
老师只讲了求解利用Floyed求解任意两点的最短路径值,却没有求解任意两点最短路径的具体路径是什么。通过自己的思考实现了,在此分享给大家(提出想着加个pre发现是不行的,因为pre的状态会被不停的更新,导致求出来的结果就错了)
解决思路:
1.假定:起始点为s,终止点为e
2.从起始点s,确定最短距离的点假如为t,那么就存在dis[s][t] == g.getWeight(s,t) + dis[t][e]
3.然后就s=t,再从剩下的s-e 依次求解,继续从第1步开始循环执行,直到找不到最短距离的t点,退出循环。
简化理解:从一个路径中不停的确定第一个点,然后再从剩余的路径中再确认一个点,最终就把起始点s、中间点、终点e,拼接起来就是任意两点的最短路径了。老师我这思路没有错吧?
class Floyed {
constructor(g) {
this._g = g;
this._hasNegativeCycle = false;
this.dis = Array(g.V())
.fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
.map(() => Array(g.V()).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER));
this.next = Array(g.V())
.fill(-1)
.map(() => Array(g.V()).fill(-1));
for (let v = 0; v < g.V(); v++) {
this.dis[v][v] = 0;
for (let w of g.adj(v)) {
this.dis[v][w] = g.getWeight(v, w);
//! next[v][w]表示:v->w这条边的终点(初始:就是v->w 直连边,终点就是w)
this.next[v][w] = w;
}
}
//! 计算任意两点直接的最短距离
for (let t = 0; t < g.V(); t++) {
for (let v = 0; v < g.V(); v++) {
for (let w = 0; w < g.V(); w++) {
if (this.dis[v][t] != Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER && this.dis[t][w] != Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER && this.dis[v][t] + this.dis[t][w] < this.dis[v][w]) {
this.dis[v][w] = this.dis[v][t] + this.dis[t][w];
//! 说明:能找到一个中间点t,能更近的抵达w点。那么就更新next[v][w]的值
//! 其实就是更新这条边的终点,让其通过next[v][t]这条边(终点)更近的边抵达终点w
this.next[v][w] = this.next[v][t];
}
}
}
}
for (let v = 0; v < g.V(); v++) {
if (this.dis[v][v] < 0) {
this._hasNegativeCycle = true;
break;
}
}
}
hasNegativeCycle() {
return this._hasNegativeCycle;
}
disTo(v, w) {
this._g.validateVertex(v);
this._g.validateVertex(w);
return this.dis[v][w];
}
isConnectTo(v, w) {
return this.dis[v][w] != Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
}
getLocation(k) {
let s = (k / this._g.V()) | 0;
let e = k % this._g.V();
return { s, e };
}
pathTo1(v, w) {
if (!this.isConnectTo(v, w)) {
return [];
}
//! 自己到自己,直接返回
if (v == w) {
return [];
}
let s = v;
let e = w;
let path = [];
path.push(s);
while (true) {
//! 是否能找到确定的第一个最短点
let isCanFindMidPoint = false;
for (let t = 0; t < this._g.V(); t++) {
if (t == s || t == e) {
continue;
}
//! 确定一个最短点 + 最短点至终点的最短距离
if (this._g.hasEdge(s, t) && this._g.hasEdge(t, e) && this.dis[s][e] === this._g.getWeight(s, t) + this.dis[t][w]) {
path.push(t);
s = t;
isCanFindMidPoint = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isCanFindMidPoint) {
break;
}
}
path.push(e);
return path;
}
pathTo2(v, w) {
if (!this.isConnectTo(v, w)) {
return [];
}
//! 自己到自己,直接返回
if (v == w) {
return [];
}
let s = v;
let e = w;
let path = [];
path.push(s);
while (true) {
//! 是否能找到确定的第一个最短点
let isCanFindMidPoint = false;
for (const t of this._g.adj(s)) {
if (this._g.hasEdge(s, t) && this._g.hasEdge(t, e) && this.dis[s][e] === this._g.getWeight(s, t) + this.dis[t][w]) {
path.push(t);
s = t;
isCanFindMidPoint = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isCanFindMidPoint) {
break;
}
}
path.push(e);
return path;
}
/* 参考实现:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/finding-shortest-path-between-any-two-nodes-using-floyd-warshall-algorithm/ */
pathTo(v, w) {
if (!this.isConnectTo(v, w)) {
return [];
}
//! 自己到自己,直接返回
if (v == w) {
return [];
}
let path = [];
path.push(v);
while (v != w) {
v = this.next[v][w];
path.push(v);
}
return path;
}
}
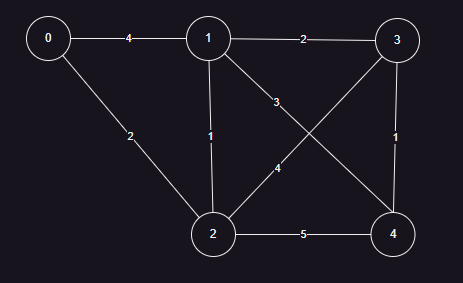
测试代码
let g = new WeightedGraph(resolve(__dirname, "assets/g.txt"));
let floyed = new Floyed(g);
if (!floyed.hasNegativeCycle()) {
for (let v = 0; v < g.V(); v++) {
for (let w = 0; w < g.V(); w++) {
console.log(`${v}-${w}:`, floyed.disTo(v, w));
console.log(`${v}-${w} path:`, floyed.pathTo(v, w));
}
console.log("-------------------------------");
}
} else {
console.log("graph has negative cycle !");
}
测试结果:
0-0: 0
0-0 path: []
0-1: 3
0-1 path: [ 0, 2, 1 ]
0-2: 2
0-2 path: [ 0, 2 ]
0-3: 5
0-3 path: [ 0, 2, 1, 3 ]
0-4: 6
0-4 path: [ 0, 2, 1, 3, 4 ]
-------------------------------
1-0: 3
1-0 path: [ 1, 2, 0 ]
1-1: 0
1-1 path: []
1-2: 1
1-2 path: [ 1, 2 ]
1-3: 2
1-3 path: [ 1, 3 ]
1-4: 3
1-4 path: [ 1, 3, 4 ]
-------------------------------
2-0: 2
2-0 path: [ 2, 0 ]
2-1: 1
2-1 path: [ 2, 1 ]
2-2: 0
2-2 path: []
2-3: 3
2-3 path: [ 2, 1, 3 ]
2-4: 4
2-4 path: [ 2, 1, 3, 4 ]
-------------------------------
3-0: 5
3-0 path: [ 3, 1, 2, 0 ]
3-1: 2
3-1 path: [ 3, 1 ]
3-2: 3
3-2 path: [ 3, 1, 2 ]
3-3: 0
3-3 path: []
3-4: 1
3-4 path: [ 3, 4 ]
-------------------------------
4-0: 6
4-0 path: [ 4, 1, 2, 0 ]
4-1: 3
4-1 path: [ 4, 3, 1 ]
4-2: 4
4-2 path: [ 4, 1, 2 ]
4-3: 1
4-3 path: [ 4, 3 ]
4-4: 0
4-4 path: []
-------------------------------
770
收起













